Risk Management
General Principles for Risk Management
SMFL recognizes the importance of risk management and identifies the locations and types of risks to be managed according to our strategic objectives and business activities. In accordance with the following general principles, SMFL conducts appropriate management according to the characteristics of each risk.
- Group-level management
- Various risks are managed at the SMFL Group level to avoid infringement of laws, regulations and other rules in accordance with the nature and importance of the business.
- Management based on quantification
- SMFL identifies the range of risks to be managed and quantitatively manages them according to the characteristics of the risks.
- Ensuring consistency with business strategy
- Risk management shall be consistent with business strategy.
- System of checks
- The risk management system shall be designed to check operations.
- Response in case of emergency or serious situation
- If risk materializes, SMFL takes necessary measures based on the assumption of situations and scenarios that have a significant impact on management and financial conditions.
- Verification of the risk management system
- The internal audit division examines our risk management system.
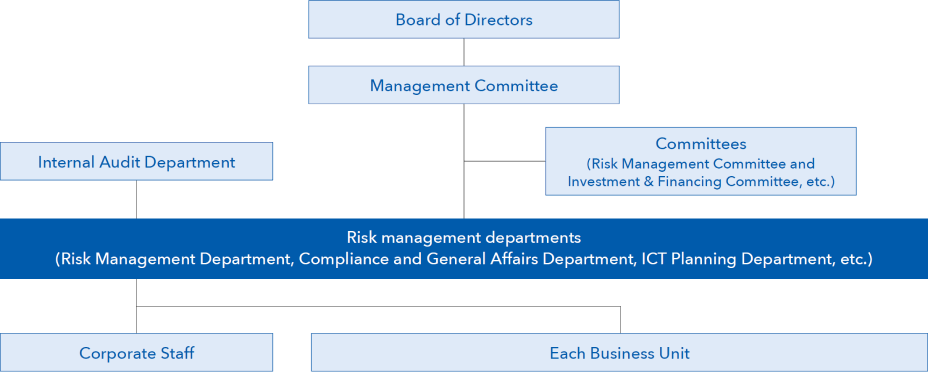
Three Lines Model
We are working to strengthen our risk management based on the three lines model concept, which is a framework for risk governance.
| Main Departments | Roles and Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| First Line Business departments, etc. |
As the risk owner for the business under his/her jurisdiction, he/she will assume the following roles and responsibilities in accordance with the basic policies established by the risk management departments (second line).
|
| Second Line Risk management departments |
To improve the risk management system within SMFL, the following roles and responsibilities will be assumed:
|
| Third Line Internal Audit Department |
From a position independent of the first and second lines, this department evaluates and verifies whether first and second line activities are being carried out effectively and appropriately. The results of these investigations will be reported to the Board of Directors and Management Committee, etc., and recommendations for improvements made for any issues or problems uncovered, as well as advice given to relevant departments as necessary. |
Risk Management System
Risk Management Methods
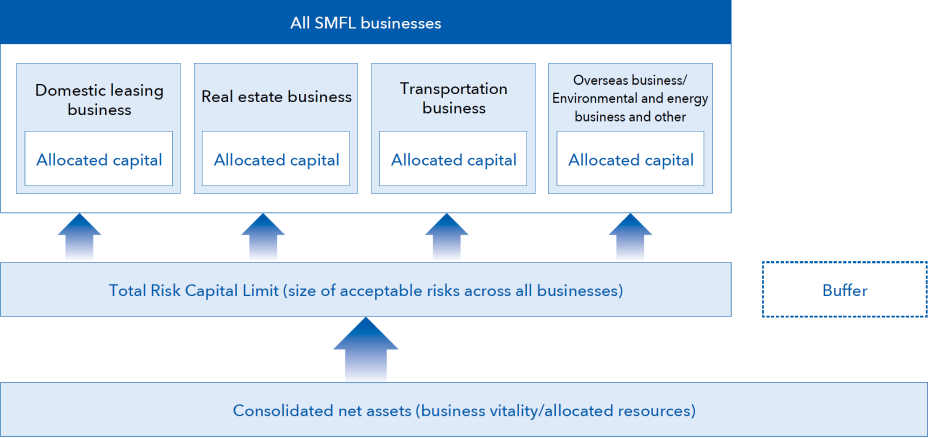
Risk capital management
In order to balance risks and returns while controlling risks within the limit of business vitality without placing undue emphasis on specific risks, we ascertain the amount of risk as much as possible, and set an upper limit on the size of acceptable risks as the "Total Risk Capital Limit."
SMFL's risk capital management
Risk Capital
We define "risk capital" as the approximate maximum loss exposure on owned assets, which is covered by capital.

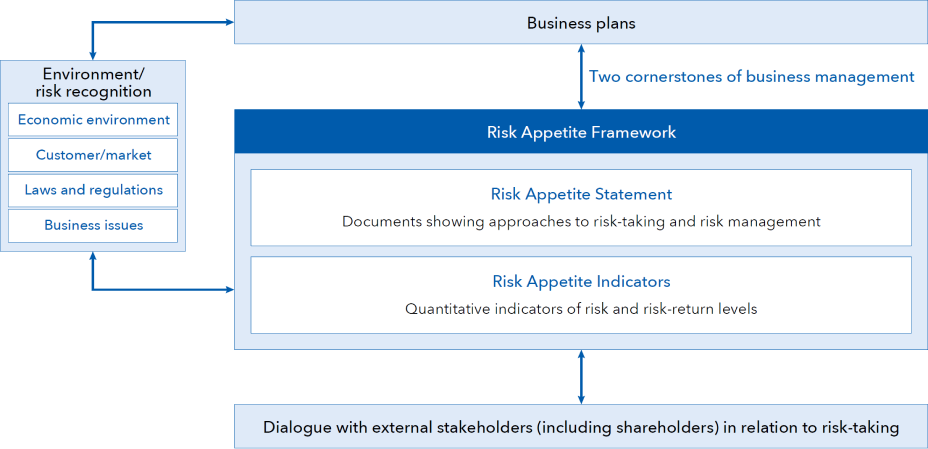
Risk Appetite Framework
SMFL has adopted the Risk Appetite Framework as our management structure in order to clarify the types and amounts of risk associated with earnings growth and to disseminate them throughout SMFL.
The Risk Appetite Framework is broadly divided into two components: Risk Appetite Statement and Risk Appetite Indicators (see the diagram on the right).
Using these documents and indicators, SMFL conducts Company-wide reviews of the risks and reflects them in our management strategy to promote appropriate risk-taking and to aim for business operations that balance soundness, profitability, and growth potential.
Structure of Risk Appetite Framework
Stress Tests
SMFL is developing and enhancing stress testing methods to proactively verify the impact of unforeseen events such as a large-scale deterioration in economic conditions or a worsening of the market conditions in a specific industrial sector on our credit portfolio and financial position including shareholders' equity, as well as cash flows. Stress tests enable us to maintain the soundness of our business even under stressed conditions, thereby allowing us to establish a system that ensures appropriate risk control under normal circumstances.
Risk Register
In anticipation of venturing into new business fields and coping with rapid shifts in the business environment, we conduct risk identification by means of a Risk Register designed to enhance risk governance and risk ownership. Business units communicate with risk management departments to identify potential business risks. SMFL has established a system whereby each business department identifies the risks inherent in its operations through communication with the risk management department, fully evaluates them and verifies the appropriateness of control measures before promoting operations that reflect them in its business strategy.

